Managing Customer Value is Critical to Achieving Full Profit Potential
“The value decade is upon us”, stated Jack Welch, CEO of General Electric in 1992 when describing one of the key trends of the 1990’s. It is generally accepted today that for a company to grow and achieve its full profit potential it must maximize customer value. Even though we are well into the value decade, there still remains much confusion as to:
- What is meant by customer value?
- How do you measure customer value?
- How do you manage customer value?
“The value decade is upon us”, stated Jack Welch, CEO of General Electric in 1992 when describing one of the key trends of the 1990’s.
It is generally accepted today that for a company to grow and achieve its full profit potential it must maximize customer value. Even though we are well into the value decade, there still remains much confusion as to:
- What is meant by customer value?
- How do you measure customer value?
- How do you manage customer value?
To the first question, “What is customer value?” We have developed a definition (see box) which underlies its work with clients. Understanding what customer value is will be discussed further on Pg. 2 of this newsletter.
Instrumental in managing customer value, is the question of “How to measure customer value?” As the saying goes, “You can’t manage what you don’t measure”. In the feature article on Pg. 2-3 of this newsletter, we have outlined the key elements of value from the customer’s perspective, together with a useful approach to assist you in beginning to measure the value delivered to customers relative to competition.
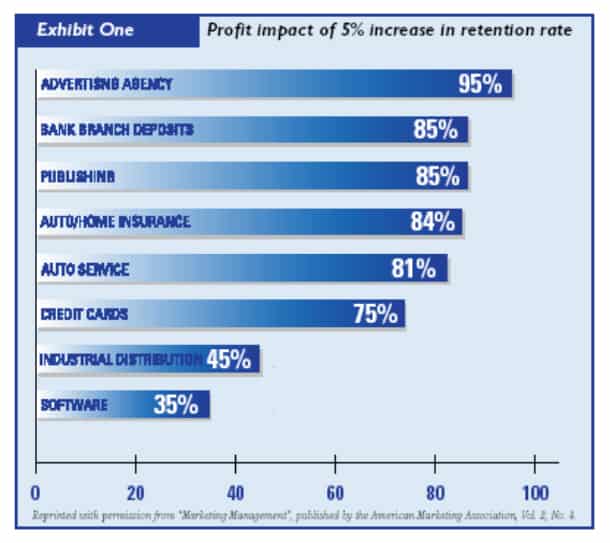
Finally as to “How you manage customer value?” this is dependent upon what you are trying to achieve. It is important to understand how a company grows and the different roles that value plays in this. For example, the role varies depending on whether: you are trying to acquire new customers; enhance the profi tability of existing customers; or, extend the duration of customer relationships. (See chart on previous page.)
CUSTOMER VALUE IS …
In setting out to manage customer value, you may grapple fi rst with the concept of how customers perceive value. The defi nition on the preceding page is an all encompassing starting point but to clarify how customers perceive value, the diagram summarizes the four foundations of perceived value: Product Quality, Service Quality, Brand Image and Personal Cost.
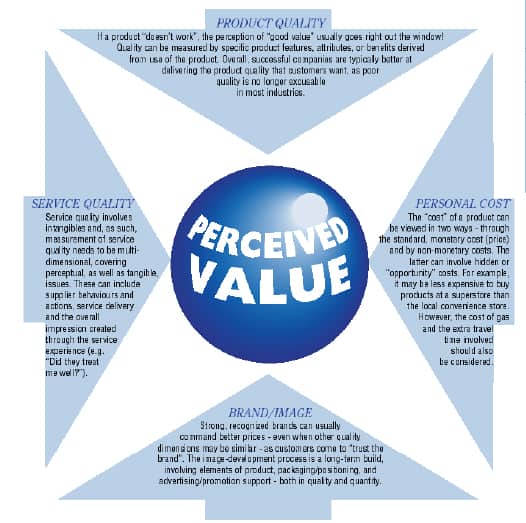
Companies that are successful at determining customer value are good at properly weighting the four value foundations and then determining the specifications that will create the benefi ts the customer is seeking. Developing specifi cations that link to the appropriate benefi ts involves answering the
following questions for each of the four foundations:
- What are the benefi ts/consequences that the customer is seeking?
- Which attributes will create those benefi ts/consequences?
- What specifications will ensure we deliver on those attributes?
In future newsletters we will provide further insights into how to answer these questions.
MEASURING CUSTOMER VALUE
Understanding what is meant by customer value is only the fi rst step. The following is a systematic approach to measuring customer value referred to as the Perceived Value Measurement Model. It is based upon sound research and can be an extremely powerful management tool. It is a four step
process:
Identifying key value drivers;
2)Weighting these key value drivers;
3) Benchmarking yourself against competitors; and,
4) Analyzing the results and taking action.
The following example illustrates a simplifi ed approach for measuring perceived customer value. In real world situations, perceived value should be measured both at the benefi ts/consequences and at attribute levels. However, in this example, we will limit measurement to the attribute level.
EXAMPLE
Company: Mega Corp
Industry: Hotels
Core Market: Business Customers
Situation: Executives of Mega Corp are trying to improve the competitiveness of one of their hotels versus a nearby competitor (Hotel X)
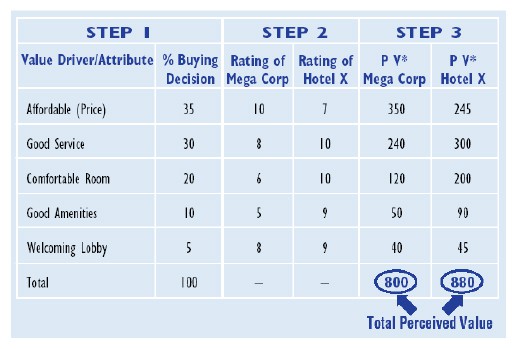
Step 1. Identify the attributes which drive value for business customers and influence their buying decisions.
The company undertook Customer Value Determination (CVD) research which identified the value drivers of this customer segment. The table below lists these value drivers as attributes derived from this research and the degree to which they infl uence the buying decision.
Step 2. Determine how customers rate you vs. competitors on these value drivers.
Customer satisfaction research and competitive benchmarking show how business customers rate Mega Corp against the competition on the key value drivers (see Step 2 of table).
Step 3. Determine your total perceived value (P V)* relative to competitors.
Perceived value is calculated for both hotels by determining the weighted average of the importance weighting and performance score (ie., Step 1 x Step 2 = P V measurement). (See Step 3 of the table.)
Step 4. Analyze the results and take action.
In this case the results indicate that Hotel X is delivering the most value to the business customer market segment (880 vs. 800). This is the case even though it has the highest price. Better service, more comfortable rooms and better amenities are giving it a value edge. Because Hotel X is delivering more value it will gain market share while Mega Corp will lose market share.
To offset the lower value rating of their hotel, the Mega Corp hotel executives must now identify how they are going to go about improving the position of their hotel relative to its competitor. If they do not wish to lower price even further then they must do one of the following:
- Improve its performance rating on the other attributes;
- Try to alter the attributes used by the customer to determine value (e.g., introduce a loyalty
program); or, - Target segments of the market which are more price sensitive.